What Are Fair Value Gaps and How to Trade Them
Fair value gaps are hidden clues left behind when the market moves too fast. In this beginner-friendly guide, you'll learn what fair value gaps are, why they matter, and how to trade them with confidence using simple chart setups—even if you're just starting out.

"An investment in knowledge pays the best interest."
— Benjamin Franklin
If you’ve been learning about trading or forex, you might have come across a term that sounds complex but is actually quite simple when broken down: fair value gaps. These gaps are often overlooked by beginners, but they can give you a big edge if you know how to spot and trade them properly. This article is your full guide to understanding what fair value gaps are, why they matter, and how to use them in your trading strategy.
Key Takeaways
- Fair value gaps are price areas on a chart that the market skipped during fast movements.
- They are often revisited, making them useful zones for trade entries.
- FVGs are caused by imbalances such as breaking news, big orders, or sudden breakouts.
- Traders look for gaps using three-candle formations and confirm trades with price action.
- Fair value gaps work best with other tools like support/resistance and trend direction.
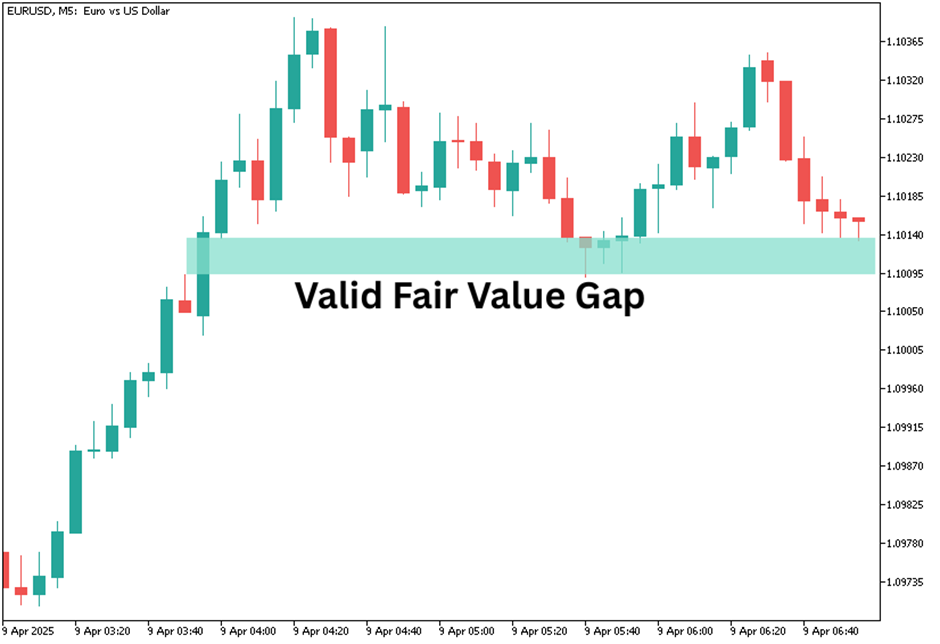
What Is a Fair Value Gap?
A fair value gap (FVG) happens when price moves so quickly in one direction that it skips certain price levels. These skipped levels create a gap on the chart that didn’t have any trading activity.
Here’s a simple way to think about it: Imagine running across a sandy beach and skipping a few footprints. Those missing steps are like the prices that didn’t get filled called the fair value gap.
Fair value gaps are most commonly spotted using three candlesticks. When price moves quickly, the second candle opens higher or lower than the first candle’s close, leaving a blank space in between. That space is the gap. Fair value gaps can form in both bullish (upward) and bearish (downward) trends, and recognizing them gives traders an idea of where price may return to before continuing.
Why Do Fair Value Gaps Happen?
Fair value gaps are caused by market imbalances. These imbalances occur when there is a lot more buying or selling than the market can handle at a specific price range. As a result, the market skips over price levels without enough time for buyers and sellers to match.
Some common causes include:
- Important news releases (like central bank decisions or job reports)
- Sudden changes in sentiment
- Large institutional orders that create a surge in demand or supply
When price surges, it sometimes leaves behind areas that haven't been tested or traded. That untested area is what we call the fair value gap.
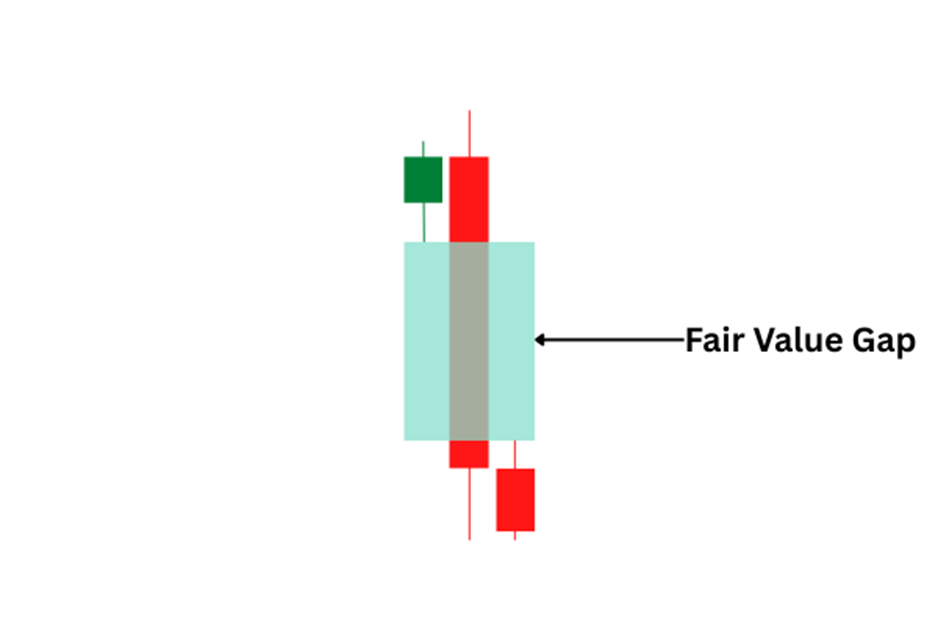
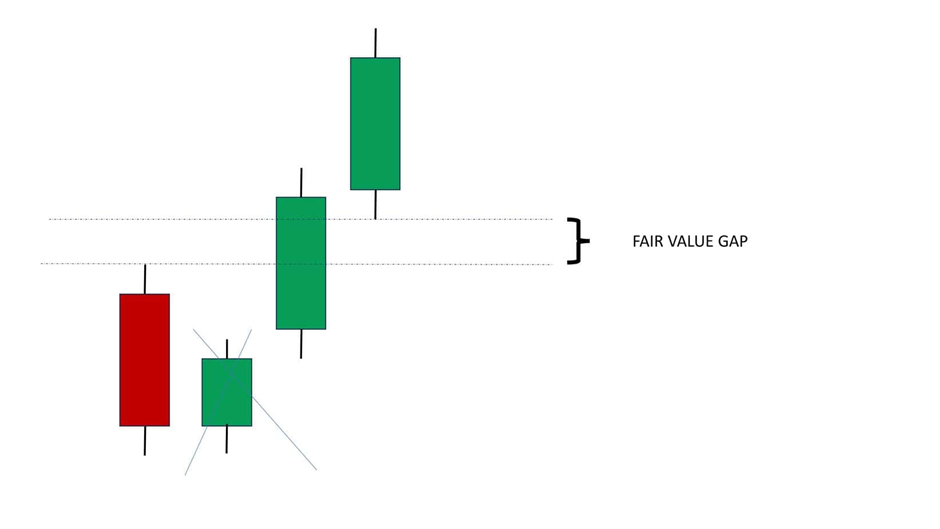
Spotting Fair Value Gaps on the Chart
To spot a fair value gap, look for three candles:
- The first candle represents the original price activity.
- The second candle moves sharply in one direction, leaving space between it and the first candle.
- The third candle confirms the move, while the gap between the first and second candle becomes the fair value gap.
Let’s say a bullish fair value gap appears:
- Candle A closes at 1.1000
- Candle B opens at 1.1015 and closes at 1.1050
- Candle C continues upward
The gap between 1.1000 and 1.1015 is where the market didn’t trade. This area may be revisited.
A fair value gap is not just about the candles as it's also about market structure. Gaps that occur near support or resistance zones tend to have higher importance.
Bullish vs Bearish Fair Value Gaps
Fair value gaps work in both directions:
|
Type |
Direction |
What It Tells You |
|
Bullish FVG |
Upward |
Price moved up too fast, might pull back later |
|
Bearish FVG |
Downward |
Price dropped
fast, might bounce back up first |
A bullish FVG shows buyers were strong, but price may return to the gap before continuing up. A bearish FVG signals strong selling pressure, but price may revisit the gap before dropping again.
How to Trade a Fair Value Gap
Trading a fair value gap is about patience. You wait for price to return to the gap and then look for signs that the market might continue in the original direction.
Step 1: Mark the Gap
Use a rectangle tool on your trading platform to highlight the fair value gap. This helps you keep an eye on it.
Step 2: Wait for Price to Return
Don’t jump in right away. Wait for the price to come back into the gap zone. The return might happen quickly or after several hours or days.
Step 3: Look for Confirmation
This could include:
- A bullish candle inside a bullish gap zone
- A bearish rejection in a bearish gap
- RSI or MACD divergence
Step 4: Enter the Trade
Enter your buy or sell position once you see confirmation.
- Place your stop-loss just beyond the gap.
- Set your take-profit based on recent highs/lows or a fixed ratio like 1:2.
For example, if you're buying, your stop-loss might go just below the bottom of the gap, and your target could be the next resistance.
Combining Fair Value Gaps with Other Strategies
Fair value gaps become more powerful when you combine them with:
- Trend analysis: Trade in the direction of the trend for higher chances of success.
- Key support and resistance levels: Gaps near these levels are more likely to work.
- Volume analysis: High volume near the gap often confirms market interest.
Let’s say you spot a bullish FVG in an uptrend and near support. That’s a strong setup. But if it’s in a downtrend, you might want to stay away or wait for stronger confirmation.
Example Trade Using a Fair Value Gap
Imagine you're looking at GBP/USD on the 1-hour chart:
- Price drops fast from 1.2750 to 1.2700 in two candles, skipping prices from 1.2730 to 1.2710
- A gap is formed between 1.2730 and 1.2710
- Hours later, price climbs back into that gap zone
- A bearish engulfing candle appears at 1.2730
You could enter a sell trade at 1.2725, place a stop-loss at 1.2740, and aim for 1.2680. The gap acted as resistance, and you used confirmation to time your trade.
Mistakes to Avoid with Fair Value Gaps
Fair value gaps are helpful, but they’re not magic. Here are some common mistakes traders make:
- Trading every gap: Not all gaps are worth trading. Wait for good setups.
- Ignoring market direction: Trading a bullish gap in a downtrend is risky.
- Skipping confirmation: Jumping in too early can lead to losses.
- Forgetting stop-losses: Always protect yourself. Gaps can fail.
Being patient and combining fair value gaps with strong trading rules can make all the difference.
Conclusion
Fair value gaps give traders a deeper understanding of how price moves and where the market might return. They show us areas where the market moved too fast and may need to come back. If used correctly, they can give you strong trade entries with good risk-reward setups.
Keep practicing by spotting fair value gaps on your charts. Use them with trend direction, support and resistance, and always wait for confirmation. In time, you’ll become more confident in your trading decisions.
Want deeper insights on forex strategies? Check out our blog for more tips to up your trading game.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a fair value gap in simple terms?
A fair value gap is a price zone where the market moved so fast it didn’t trade certain prices. This creates a visible “gap” on the chart.
2. Do all fair value gaps get filled?
No, not all of them. Some get filled quickly, others take time, and a few never get filled at all.
3. Can fair value gaps work in any market?
Yes. You can find them in forex, stocks, crypto, and even commodities. They follow the same logic everywhere.
4. What timeframe is best for spotting FVGs?
Higher timeframes like the 1-hour, 4-hour, or daily charts tend to show more reliable fair value gaps.
5. Is trading fair value gaps risky?
Like all strategies, it carries risk. That’s why it’s important to wait for confirmation and use stop-losses.




