Understanding Market Volatility: What It Is and How to Trade It
Volatility creates both opportunity and danger. Learn how to navigate volatile markets with the right tools, mindset, and strategy to trade confidently.

“In the midst of chaos, there is also opportunity.” — Sun Tzu
The market goes up and down every day. Sometimes, it moves fast. That’s called volatility. When the market is very volatile, prices can change a lot in just a few minutes. This can be scary but it can also be a chance to make money.
In this blog, you’ll learn what volatility is, what causes it, and how to trade when things get crazy.
Key Takeaways
- Volatility reflects how fast and unpredictably price moves. It's not always a bad thing as traders can still profit from it.
- Tools like the VIX and ATR help gauge volatility levels in real time.
- Strategies must adapt based on whether the market is stable, moderately volatile, or highly volatile.
- Avoid over-leveraging during volatile periods, as whipsaws and false breakouts are common.
- Volatility spikes are often triggered by macroeconomic events, news, earnings reports, or geopolitical developments.
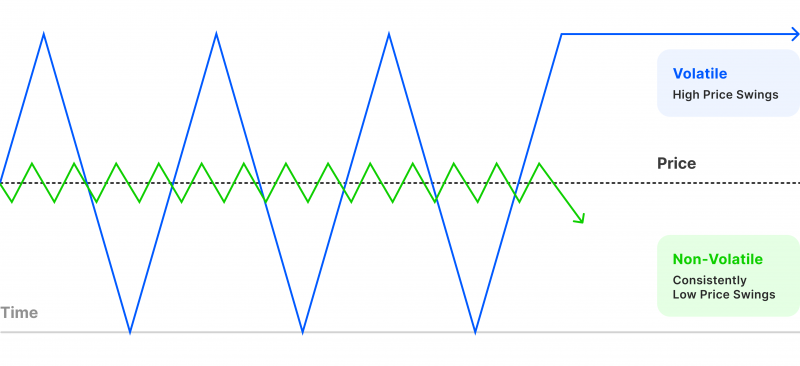
What Is Market Volatility?
Volatility refers to the degree of variation in a trading instrument’s price over time. In simple terms, it's how “wild” the price action is.
- Low Volatility: Price moves gradually or in a tight range
- High Volatility: Price moves quickly, with large swings and little predictability
Measured statistically, volatility reflects the standard deviation of returns but practically, traders know it as the feeling of chaos in the charts.
Recent Examples of Market Volatility (2024–2025):
- March 2024: U.S. CPI report exceeded expectations, triggering a 3.4% drop in the Nasdaq within two hours.
- October 2024: Escalation of geopolitical tensions in the Middle East caused crude oil to spike 8% in a single trading day.
- January 2025: Tech stocks plunged following disappointing Q4 earnings from major firms like Meta and Alphabet, pushing VIX to above 24.
Causes of Volatility
Several factors can spike volatility, including:
- Economic News Releases (CPI, GDP, Fed decisions)
- Earnings Reports
- Geopolitical Events (wars, elections, pandemics)
- Interest Rate Changes
- Unexpected Market Shocks (like the COVID crash)
Even rumors or sentiment shifts can inject short-term turbulence into otherwise stable markets.
The VIX: Wall Street’s Fear Gauge
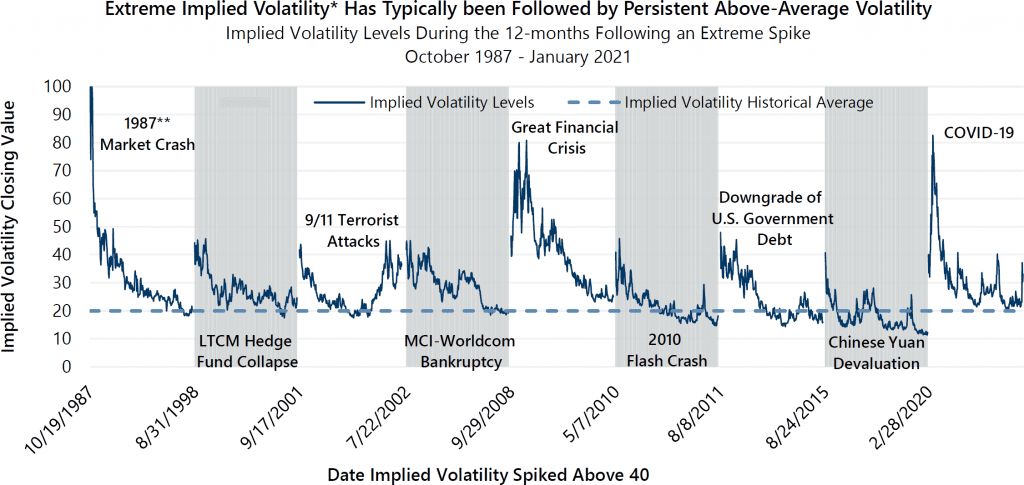
The VIX Index (CBOE Volatility Index) measures market expectations for volatility over the next 30 days. It rises when fear spikes and falls when markets are calm.
- High VIX (above 30): Markets are fearful, uncertainty is high
- Low VIX (under 15): Markets are calm, trend-following thrives
Check it daily before trading — it can tell you if you're entering a landmine zone or a calm trend.
📖 Learn more about the VIX on Investopedia
How Volatility Affects Trading
- Wider Spreads: Brokers may widen the bid-ask spread during volatile periods
- Slippage: Orders may fill at worse prices than expected
- Emotional Traps: Fear and greed are amplified when prices spike fast
- Technical Breakouts and Fakeouts: Patterns fail more often in chaotic markets
Understanding these risks is key to survival.
Strategies to Trade Volatility Successfully
1. Trade Smaller Size
High volatility = higher risk. Reduce position sizes to avoid oversized losses.
2. Use Wider Stops — But Only Strategically
You don’t want to get stopped out on normal price noise. Adjust stops accordingly, but never risk more than your max daily limit.
3. Favor Volatility-Friendly Setups
- Breakout plays
- Reversal setups after extreme moves
- Options strategies like straddles or strangles
Volatility can be your friend — but only with defined edges.
4. Stick to High-Quality Timeframes
Avoid the 1-minute madness unless you’re highly experienced. Focus on 5m, 15m, or hourly charts to better manage noise.
5. Use Volatility Indicators
- Average True Range (ATR): Measures how much an asset typically moves
- Bollinger Bands: Expand and contract based on recent volatility
- Keltner Channels: Show breakout levels during choppy price action
Mental Game: Staying Grounded in the Storm
Trading volatile markets isn’t just about charts — it’s about controlling your psychology:
- Stick to your plan. Temptation to deviate is highest during wild swings.
- Avoid revenge trading. One fast red trade can lead to four more if you’re not careful.
- Focus on execution, not outcome. Volatility doesn’t mean abandon discipline.
Long-Term Thinking in a Short-Term Storm
It’s easy to get caught up in day-to-day volatility. But the best traders zoom out. They understand:
- Not every day is a trading day
- Volatility can shift from asset to asset — adapt
- Missing a big move is better than mismanaging a bad trade
Final Word
Volatility means the market moves fast. Prices can go way up or way down. This can be scary, but it’s also a time to find good trades.
Always stay calm. Don’t chase big moves. Follow your plan, use stop-losses, and never risk too much on one trade. The more you learn about volatility, the more confident you’ll feel. Practice with small trades first.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is high volatility bad for trading?
Not necessarily. Volatility increases opportunities, but also risk. With proper risk management, volatile markets can be profitable.
Q2: What’s the best time to trade during volatile days?
Avoid the first 15–30 minutes of market open. Wait for price to settle or confirm a direction.
Q3: Can I rely solely on the VIX?
No. VIX is great for a macro view, but use indicators like ATR or Bollinger Bands for chart-specific volatility.
Q4: Should I use leverage in volatile conditions?
Use reduced or no leverage. Volatility increases risk, and leverage can multiply losses fast.
Q5: What assets are most affected by volatility?
Tech stocks, crypto, and commodities like oil and gold tend to react more sharply to global news.
🔗 External Resources:
- Investopedia: Volatility
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/v/volatility.asp - Investopedia: VIX - CBOE Volatility Index
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/v/vix.asp