Mastering Trading Psychology: Achieve Peak Performance in Trading
Trading psychology is vital for successful trading. Discover effective strategies to manage emotions, avoid common psychological pitfalls, and enhance trading performance.

“The investor’s chief problem—and even his worst enemy—is likely to be himself.” — Benjamin Graham
Trading psychology is arguably the most critical factor determining success in the trading world. While technical and fundamental analysis are essential, mastering your mindset is equally crucial. This comprehensive guide provides proven strategies to manage your trading psychology, ensuring you make informed, logical decisions rather than emotionally driven mistakes.
Key Takeaways
- Your mindset impacts your trading results more than any indicator.
- Emotions like fear and greed lead to poor decisions unless managed.
- Building psychological discipline takes time, practice, and the right tools.
- Simulated trading can help train your mind in a risk-free environment.
- Successful traders treat psychology as part of their edge, not an afterthought.
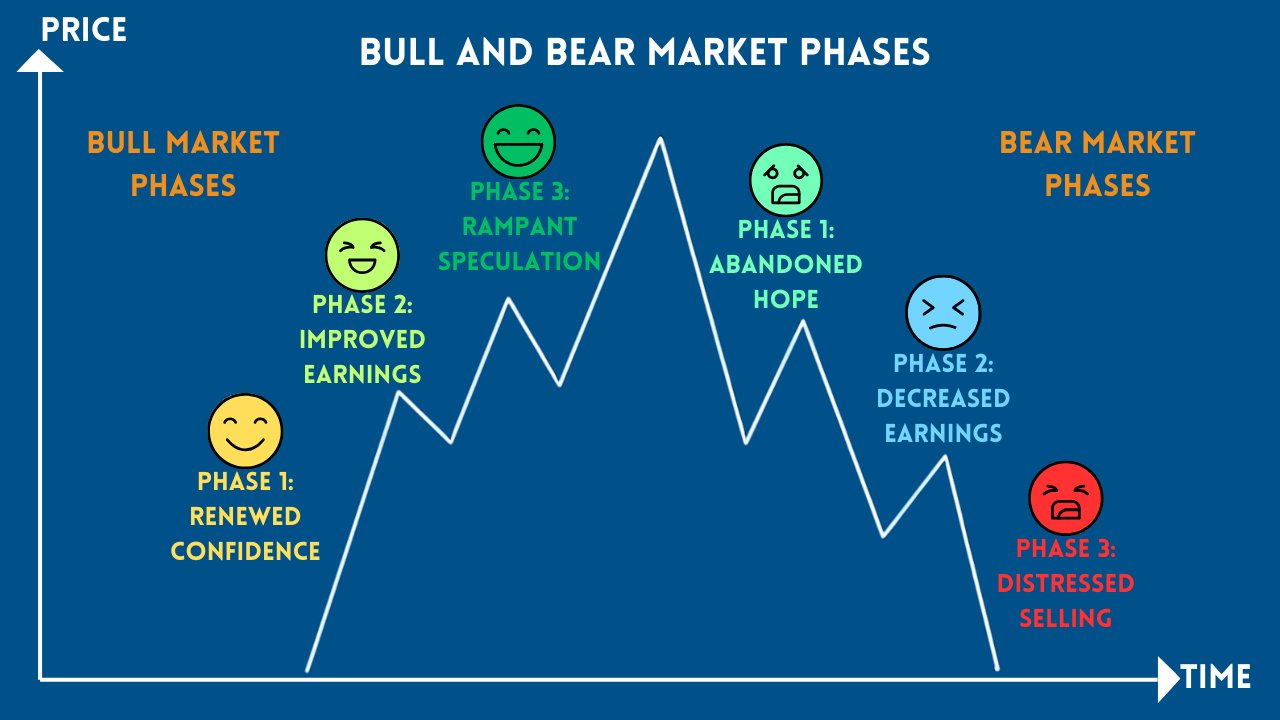
Understanding Trading Psychology
Trading psychology refers to the emotional and mental states that influence traders' decisions and behaviors. Common psychological challenges include fear, greed, impatience, overconfidence, and revenge trading. Addressing these challenges directly improves overall trading outcomes and sustainability.
Why Is Trading Psychology Important?
- Emotion Management: Helps traders avoid emotional reactions that can lead to poor decisions.
- Decision-Making: Encourages disciplined and rational trading choices.
- Stress Reduction: Promotes healthier emotional states, reducing burnout and anxiety.
- Consistency: Facilitates adherence to trading plans and strategies.
Common Psychological Pitfalls in Trading
Fear
Fear often manifests as hesitation or missed trading opportunities. It can prevent traders from entering valid setups or prematurely exiting profitable trades.
Greed
Greed can cause traders to overstay positions, aiming for unrealistic gains and neglecting sensible profit-taking strategies.
Overconfidence
After experiencing several profitable trades, traders might become overconfident, taking excessive risks and ignoring fundamental risk management.
Revenge Trading
Revenge trading involves immediately attempting to recover losses through impulsive trades, often worsening losses.
Confirmation Bias
Traders may seek information confirming their beliefs while ignoring contradictory data, skewing objective decision-making.
Recent Research on Trading Psychology
A 2023 study by the CFA Institute found that emotional self-awareness and impulse control were the two most predictive traits of long-term trading consistency. Traders who used reflection techniques and kept psychological journals reported better trade filtering and exit timing.
Dr. Brett Steenbarger, a trading psychologist, says:
“Great traders don’t control their emotions — they use their emotions as information.”
This means learning to identify emotional spikes and then pausing, not reacting. That one-second pause can save your account.
Essential Techniques to Improve Trading Psychology
1. Develop and Stick to a Trading Plan
Creating a detailed trading plan outlining your strategies, entry and exit points, risk management, and trade evaluation criteria will help maintain emotional discipline.
2. Practice Mindfulness and Emotional Awareness
Regularly practicing mindfulness techniques can significantly improve emotional control. Techniques include meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness exercises.
3. Keep a Detailed Trading Journal
Documenting trades, emotions, market conditions, and decision rationale helps identify emotional patterns and psychological pitfalls, allowing continuous self-improvement.
4. Set Realistic Goals and Expectations
Establish achievable trading goals, avoiding unrealistic targets that can provoke stress and poor decision-making.
5. Continuous Education
Commit to ongoing education in trading techniques and psychological management to stay informed and resilient.

Strategies to Overcome Common Psychological Challenges
Overcoming Fear
- Proper Risk Management: Define acceptable risks per trade clearly.
- Gradual Exposure: Slowly increase your trading positions as confidence grows.
Overcoming Greed
- Set Specific Targets: Clearly define profit targets before entering trades.
- Consistent Profit Taking: Develop a disciplined approach to locking in profits.
Overcoming Overconfidence
- Maintain Humility: Acknowledge market unpredictability and your limitations.
- Regular Review: Frequently review trading outcomes and remain objective about performance.
Avoiding Revenge Trading
- Cooling-Off Periods: Step away from trading temporarily after losses.
- Reflection: Analyze losses to identify mistakes and plan corrective actions calmly.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Overtrading Recovery
Ravi, a swing trader from India, was constantly overtrading during volatile days. After journaling his emotional triggers for two weeks, he noticed he overtraded most after a losing streak. He set a personal rule: two losses and he stops trading for the day. His account, previously down 12%, recovered to breakeven in one month.
Case Study 2: Building Confidence Through Sim Practice
Lana, a beginner from the UAE, struggled with fear of entry. Her coach recommended trading in a simulated environment for 30 days, focusing only on execution, not outcome. By week 3, she could pull the trigger without hesitation and eventually transitioned to real trades with better control.
Mitigating Confirmation Bias
- Objective Analysis: Regularly challenge your assumptions and seek diverse market opinions.
- Balanced Information: Deliberately seek contradicting evidence to test your trading hypotheses.
Real-World Example of Effective Trading Psychology
Consider this practical scenario:
- Scenario: Trader faces consecutive losses, feeling frustrated and tempted by revenge trading.
- Action Taken: Steps away, performs mindfulness exercises, reviews trading journal objectively.
- Outcome: Recognizes emotional patterns, returns calmer and adheres strictly to a predefined trading plan.
Psychological Tools for Traders
- Meditation Apps: Calm, Headspace, Insight Timer
- Journaling Tools: Tradervue, Edgewonk
- Educational Resources: Books and online courses on trading psychology (e.g., "Trading in the Zone" by Mark Douglas)
Mental Training Exercises to Try
- Simulated Trading Drills – Set up a session with 10 rapid-fire chart setups. Practice identifying your entry with no money on the line. Focus on execution, not profits.
- Visualization – Before each trading session, close your eyes for two minutes and walk through your ideal trading process mentally.
- Anchor Word Technique – Pick a calming word (like “breathe” or “focus”). Say it to yourself every time your emotions spike. This trains your brain to pause and regulate.
The Role of Community and Mentorship
Engaging with trading communities and seeking mentorship provides emotional support, accountability, and valuable insights, significantly enhancing your psychological resilience.
Advanced Psychological Techniques
Visualization
Regular visualization of successful trading scenarios can enhance performance by mentally preparing traders for real-world situations.
Cognitive Behavioral Techniques
Cognitive behavioral methods help traders identify negative thought patterns and replace them with positive, constructive habits.
Stress Management
Effective stress management techniques include regular exercise, healthy sleep habits, and balanced nutrition, improving overall emotional and mental resilience.
Continuous Psychological Self-Assessment
Regular self-assessment helps traders maintain emotional awareness and discipline. Set aside specific times weekly and monthly for in-depth emotional and psychological reviews.
Internal Resources
External Resource
Final Thoughts
Mastering trading psychology is a continuous journey, crucial for trading success. By understanding emotional drivers, practicing mindfulness, maintaining disciplined risk management, and committing to ongoing psychological education, traders can significantly enhance their performance and sustainability in the markets.
Commit to your psychological growth, stay disciplined, and achieve lasting trading success.
FAQs
Q1: Can you learn trading psychology or is it natural?
A1: It’s learnable. Like any skill, it improves with practice, journaling, and feedback.
Q2: What if I keep repeating the same emotional mistakes?
A2: Identify the trigger pattern, reduce trade size, and add a journaling routine to reflect before reentering the market.
Q3: How long does it take to gain emotional control?
A3: It varies, but most traders notice progress within 4–6 weeks of consistent reflection and practice.
Q4: Do trading simulators really help with mindset?
A4: Yes. They allow you to train pattern recognition and execution without real risk, which boosts confidence.
Q5: Should I take breaks from trading when stressed?
A5: Absolutely. Trading under stress leads to poor decision-making. Step away, reset, and return when your mind is clear.